多菌灵


| 有效期 | 2年 |
| EC | EINECS 234-232-0 |
| MDL | MFCD00055390 |
| InChIKey | TWFZGCMQGLPBSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C9H9N3O2/c1-14-9(13)12-8-10-6-4-2-3-5-7(6)11-8/h2-5H,1H3,(H2,10,11,12,13) |
| PubChem CID | 25429 |
| 别名 | 防霉宝;贝芬替 |
| 英文名称 | Carbendazim |
| CAS | 10605-21-7 |
| 分子式 | C9H9N3O2 |
| 分子量 | 191.19 |
| 储存条件 | 2-8℃ |
| 纯度 | ≥98% |
| 外观(性状) | White Crystal |
| 单位 | 瓶 |
| 生物活性 | Carbendazim (Mercarzole, Carbendazole) is a broad-spectrum systemic antimycotic and can be used to control a broad range of diseases on field crops, fruits, and vegetables, including sclerotinia rot of canola, wheat head blight, peanut leaf spot, and SB on rice. Its mode of action is to inhibit the formation of mitotic microtubules in of fungi.[1-2] |
| In Vitro | Carbendazim (methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate) is widely used as a systemic fungicide in human food production and appears to act on fungal tubulin. However, it also inhibits proliferation of human cancer cells, including drug- and multidrug-resistant and p53-deficient cell lines, including murine melanoma, human breast, ovarian, lung, leukemia, and colon carcinoma cell lines, arresting the cells at the G2/M phase of the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. It inhibits the proliferation of MCF7 human breast cancer cells with IC50 of 10 μM and arrests mitosis at a similar concentration (8 μM), in concert with suppression of microtubule dynamic instability without appreciable microtubule depolymerization. With microtubules assembled in vitro from pure tubulin, carbendazim also suppresses dynamic instability, reducing the dynamicity by 50% at 10 μM, with only minimal (21%) reduction of polymer mass. Carbendazim binds to mammalian tubulin (Kd, 42.8 ± 4.0 μM)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Carbendazim (CBZ) is active in vivo against human pancreatic, lung, prostate, colon, and breast tumor xenografts. Oral administrations with CBZ at 100 and 500?mg/kg body weight for 28 days induces hepatic lipid metabolism disorder which is characterized by significant increases of hepatic lipid accumulation and triglyceride (TG) levels in mice. The serum cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein levels also increase after CBZ exposure. CBZ may also induce the occuring of inflammation characterized by the increase of serum IL-1β and IL-6 levels[2]. |
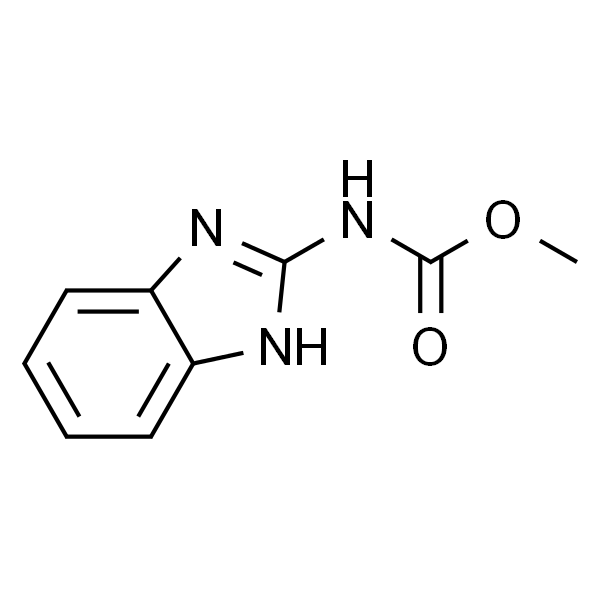
| SMILES | O=C(OC)NC1=NC2=CC=CC=C2N1 |
| 靶点 | Fungal |
| 动物实验 | Carbendazim (oral gavage; 100 and 500 mg/kg; once daily in diet; 28 days) induces hepatic lipid metabolism disorder, it results in a significant increase of hepatic lipid accumulation and triglyceride (TG) levels in mice[2]. |
| 细胞实验 | MCF7/GFP cells seeded at 3 × 104 cells/ml in six-well plates are allowed to adhere (24 h), after which the medium is replaced with medium containing carbendazim. Cells are incubated with a range of carbendazim concentrations (0.5-50 μM) for 24 h, rinsed with Versene (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1.5 mM KH2PO4, 8.1 mM Na2HPO4, 0.5 mM EDTA, pH 7.2), and detached with trypsin in Versene. Both adherent and floating cells are collected. For determination of cell proliferation, cells are stained with trypan blue and counted by hemacytometer.[1] |
| 数据来源文献 | [1] Yenjerla M, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009, 328(2):390-8. [2] Jin Y, et al. Toxicol Sci. 2015, 147(1):116-26. |
| 规格 | 500mg 1g |
是一种广谱的苯并咪唑类抗菌化合物。
使用本产品的应用案例(仅供参考)
Arabidopsis(MS Medium,0~ 0.2 mM Carbendazim)
Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with a carbendazim at 0, 0.1, and 0.2 mM was prepared and labeled as CK (control), D2, and D3 respectively.Arabidopsis seeds were disinfected and sterilized as follows: 75 %(v/v) ethanol soak for 30 s, then a 0.1 % HgCl2 disinfection for 7–10 min, followed by a wash 3–4 times in sterile water. The washed seeds were sown in the MS culture medium, and subjected to vernalization at 4 ℃ for 3 days. After vernalization, the seeds were placed in a culture room at 22 ± 2 ℃ and grown with an illumination time of 16 h d-1 at a relative humidity of 70 %. Twenty days after sowing, 100 Arabidopsis seedlings (without roots) from the same treatment groups were sheared and mixed.
来源文献:Li Z, Wang Z, Li S. Gene chip analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana genomic DNA methylation and gene expression in response to carbendazim. Biotechnol Lett. 2015 Jun;37(6):1297-307. doi: 10.1007/s10529-015-1789-1. Epub 2015 Feb 21. PMID: 25700823.
